Hip Osteoarthritis
Hip Osteoarthritis: Key Information and Care Guidelines
Key Points About Hip Osteoarthritis
- Cartilage Breakdown: Cartilage serves as a cushion in the hip joint, enabling smooth movement. In osteoarthritis, this protective layer gradually erodes due to aging, genetic factors, excess weight, joint injuries, or repetitive use.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include hip pain, stiffness, and swelling, which often worsen after activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing up from a seated position. As the condition progresses, the pain may become more persistent and constant.
Do's
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping a healthy weight helps to reduce pressure on the hip joints, thereby easing symptoms. A balanced diet and regular physical activity are key.
- Stay Active: Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling to maintain joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Consult a physical therapist to determine the best exercises for your condition.
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening the muscles around the hip, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, can enhance joint support and stability.
- Use Assistive Devices: Devices like braces, canes, or crutches can help alleviate pressure on the hip joint and improve walking stability.
- Maintain Good Posture: Proper body alignment can reduce strain on the hip. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing in positions that place stress on the joint.
Don’ts:
- Avoid Prolonged Inactivity: While rest is important during symptom flare-ups, extended inactivity can lead to muscle weakness and joint stiffness. Balance rest with gentle movement.
- Don’t Overexert: Steer clear of high-impact activities such as running or jumping, which can aggravate joint stress and increase pain.
- Limit High-Impact Sports: Activities like tennis, basketball, and jogging can be tough on the hips. Opt for low-impact exercises that boost cardiovascular health without worsening symptoms.
- Don’t Ignore Pain: Listen to your body—pain indicates that you may need to adjust your activity level or modify your movements.
- Avoid Deep Bending and Twisting: Movements involving deep hip flexion or rotation can strain the joint and worsen discomfort. Proceed with caution when performing such actions.
Physiotherapy for Hip Osteoarthritis
Physiotherapy is an essential part of managing hip osteoarthritis, aiming to alleviate pain, enhance joint function, and improve the overall quality of life for those affected. Below are common physiotherapy techniques and strategies used to address hip osteoarthritis:
- Pain Management: Physiotherapists utilize methods like heat and cold therapy, TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), and ultrasound to help control pain and provide relief.
- Exercise Programs: Tailored exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the hip, such as the hip abductors, hip flexors, and gluteal muscles. These exercises help stabilize the joint, reduce strain, and improve flexibility with range-of-motion exercises.
- Low-Impact Activities: Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming or stationary cycling helps maintain joint mobility without overloading the hip.
- Weight Management: Reducing excess body weight can decrease stress on the hip joint. Physiotherapists offer guidance on achieving a healthy weight to minimize joint strain.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like joint mobilization and soft tissue massage are used to enhance hip mobility, reduce stiffness, and ease discomfort.
- Home Exercise Programs: Physiotherapists create personalized exercise plans for patients to follow at home, ensuring long-term symptom management and continued progress.
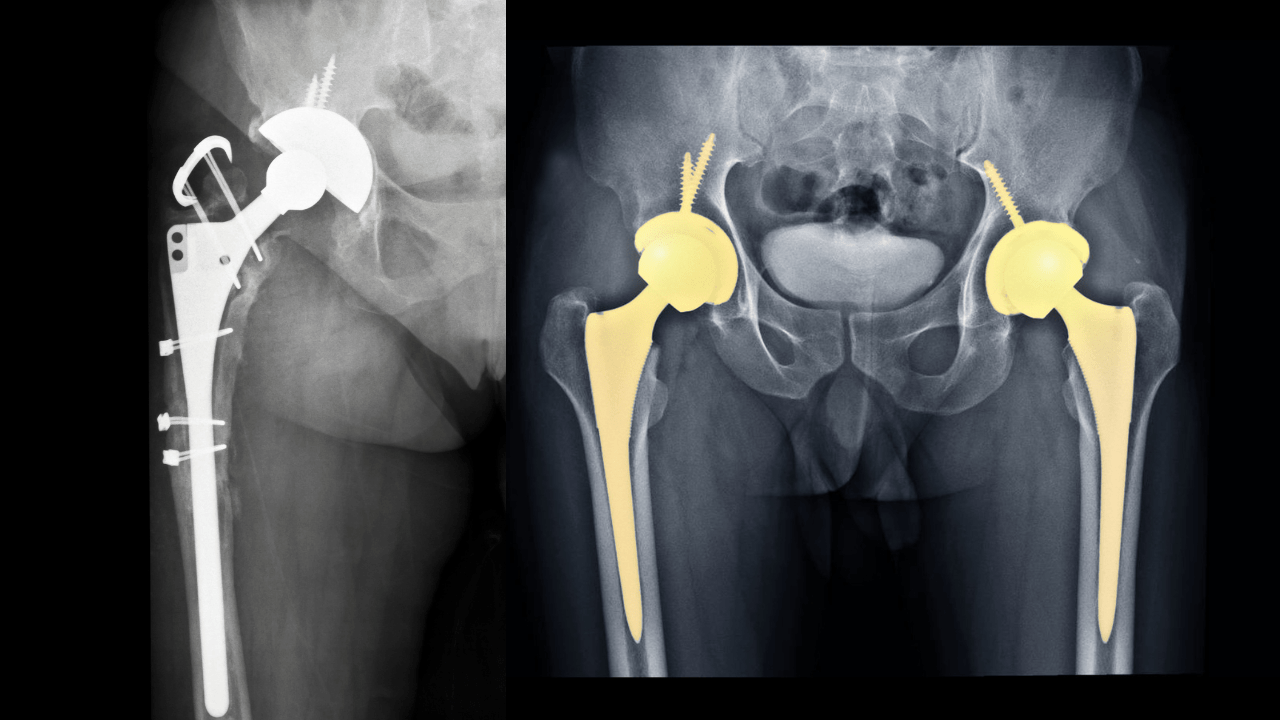
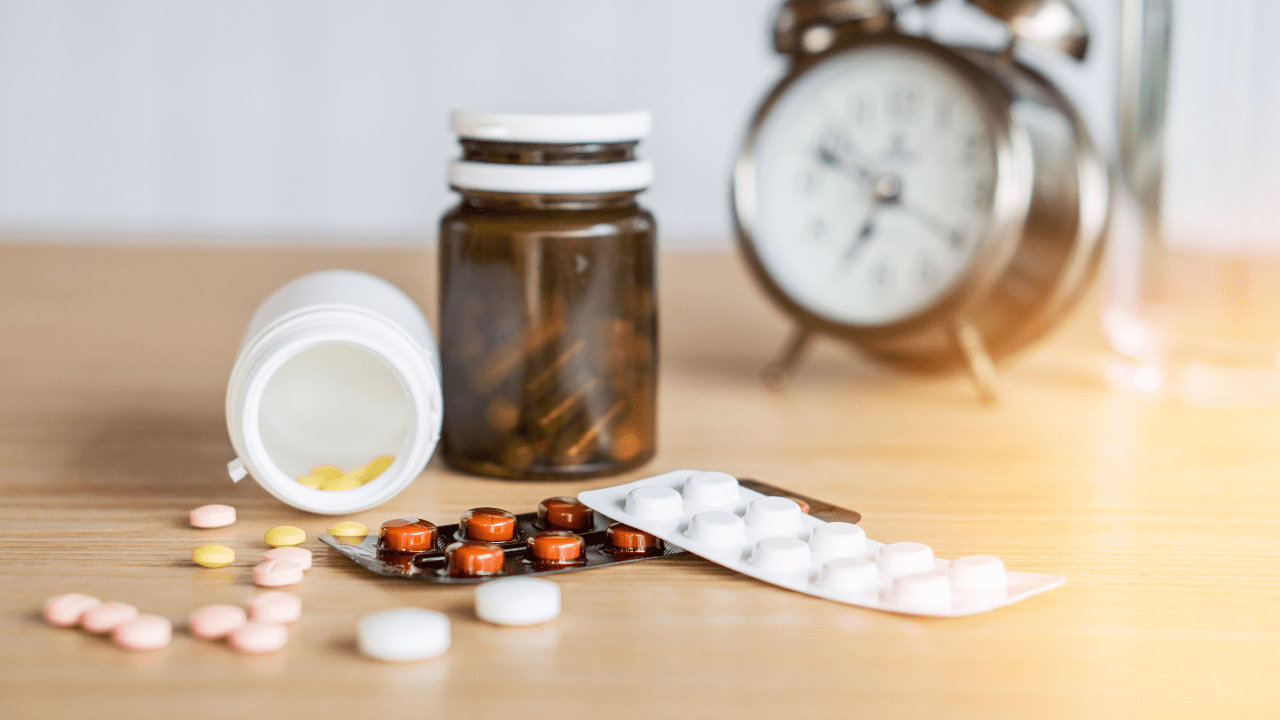
Medication for Managing Hip Osteoarthritis
Managing hip osteoarthritis typically requires a combination of non-medication and medication-based treatments. Medications play a key role in controlling pain, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function. Commonly prescribed medications include:
-
Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Often recommended as the first choice for mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis pain, acetaminophen helps relieve discomfort but has limited anti-inflammatory properties. It is generally safe when taken according to the prescribed dosage, but patients should avoid exceeding recommended amounts to prevent liver damage.
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation associated with hip osteoarthritis. These can be obtained over-the-counter or prescribed in higher doses by a doctor. Long-term use may carry risks such as gastrointestinal or cardiovascular issues, so it’s important to use them under medical supervision.
-
Short-term and Long-term Medication Use: Both short-term and long-term medications can be helpful in managing symptoms and maintaining quality of life. Discussing options with a healthcare provider ensures the best treatment plan.
Weight Management:
Weight Management:
- Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for minimizing the strain on the hip joint. Excess weight can worsen hip osteoarthritis symptoms and contribute to further joint degeneration. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce joint stress and improve overall mobility.
Exercise and Physical Therapy: Engaging in specific exercises and physical therapy can enhance joint flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and improve overall joint function. Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking are generally recommended to protect the joint while staying active.
Weight Reduction Medical Management:
- Weight reduction through medical management is often recommended for individuals who are overweight or obese and have not been able to lose weight through diet and exercise alone. This approach can significantly benefit those with hip osteoarthritis by reducing joint stress.
- Prescription Medications: Certain FDA-approved medications can support weight loss by curbing appetite, reducing fat absorption, or increasing the feeling of fullness. These medications are usually prescribed for individuals with a higher body mass index (BMI) or those with obesity-related conditions.
- Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral counseling helps individuals establish healthier eating patterns, address emotional triggers, and make sustainable lifestyle changes to support long-term weight loss goals. Combining behavioral therapy with other weight loss strategies can lead to better outcomes and improved joint health.
Discover New Heights in Healthcare with
Spire Hospital!

Address
Survey No 588, B4, 1st Floor, Ganesh Market, Jawaharlal Nehru Road, Aai Mata Mandir Chowk, Opp Market Yard Bus Depot, Bibevewadi, Pune : 411037
Phone
9175983868 / 8600159688
punehipandknee@gmail.com