Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery is a procedure where a damaged or worn-out knee joint is replaced with an artificial one, known as a prosthesis. It is commonly performed on patients with severe knee pain and mobility issues, typically due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis. Knee replacement surgery can relieve pain, restore function, and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic knee problems
Types of Knee Replacement
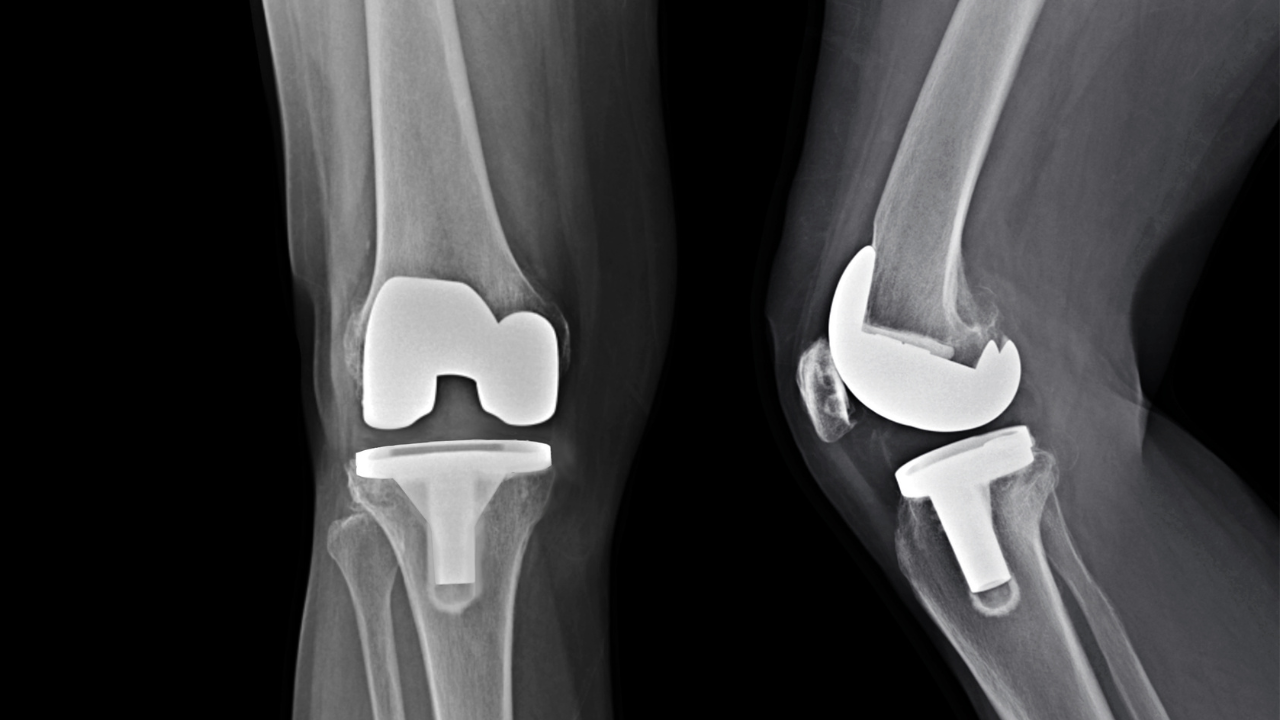
Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
In total knee replacement, the entire knee joint is replaced with a prosthesis. This involves removing the damaged cartilage and bone from the surface of the knee and replacing it with a metal or plastic implant. Total knee replacement is suitable for patients with widespread arthritis or joint damage affecting the entire knee.
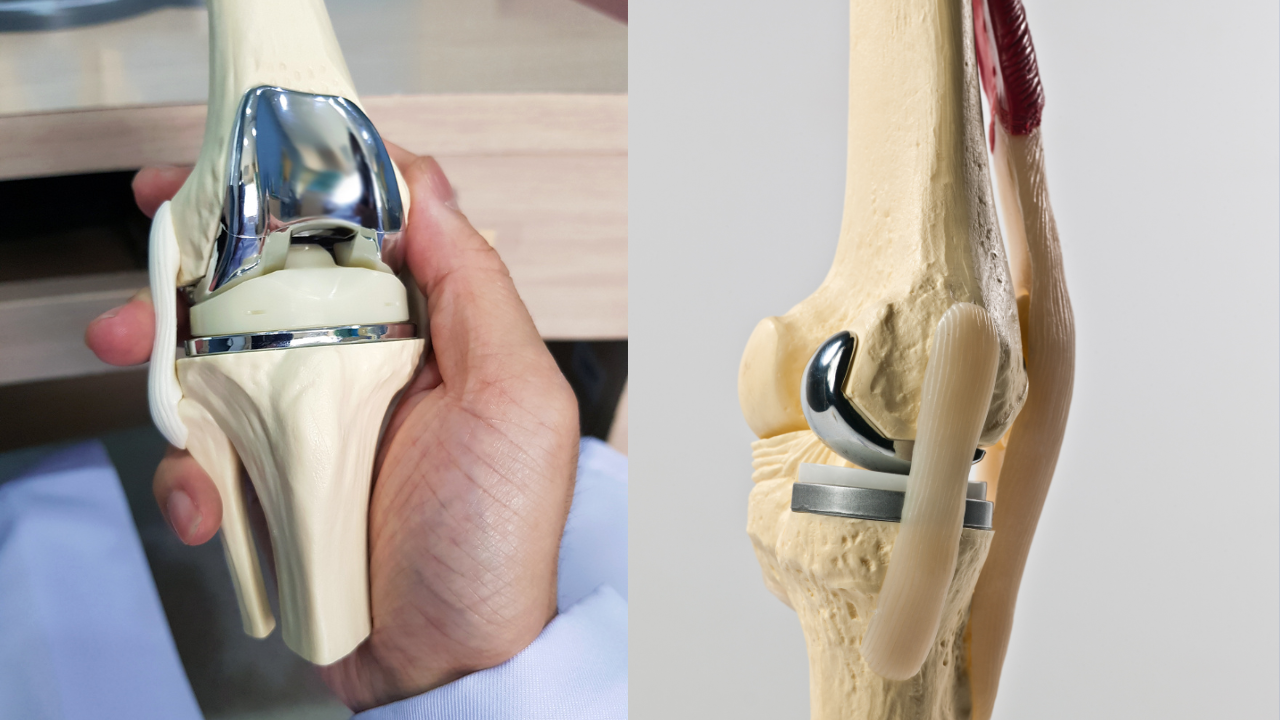
Partial Knee Replacement:
Unicompartmental knee replacement, or partial knee replacement, involves replacing only one part of the knee joint, either the inner (medial) or outer (lateral) compartment. This is recommended for patients whose arthritis or damage is limited to one compartment of the knee, allowing for a less invasive procedure and quicker recovery.
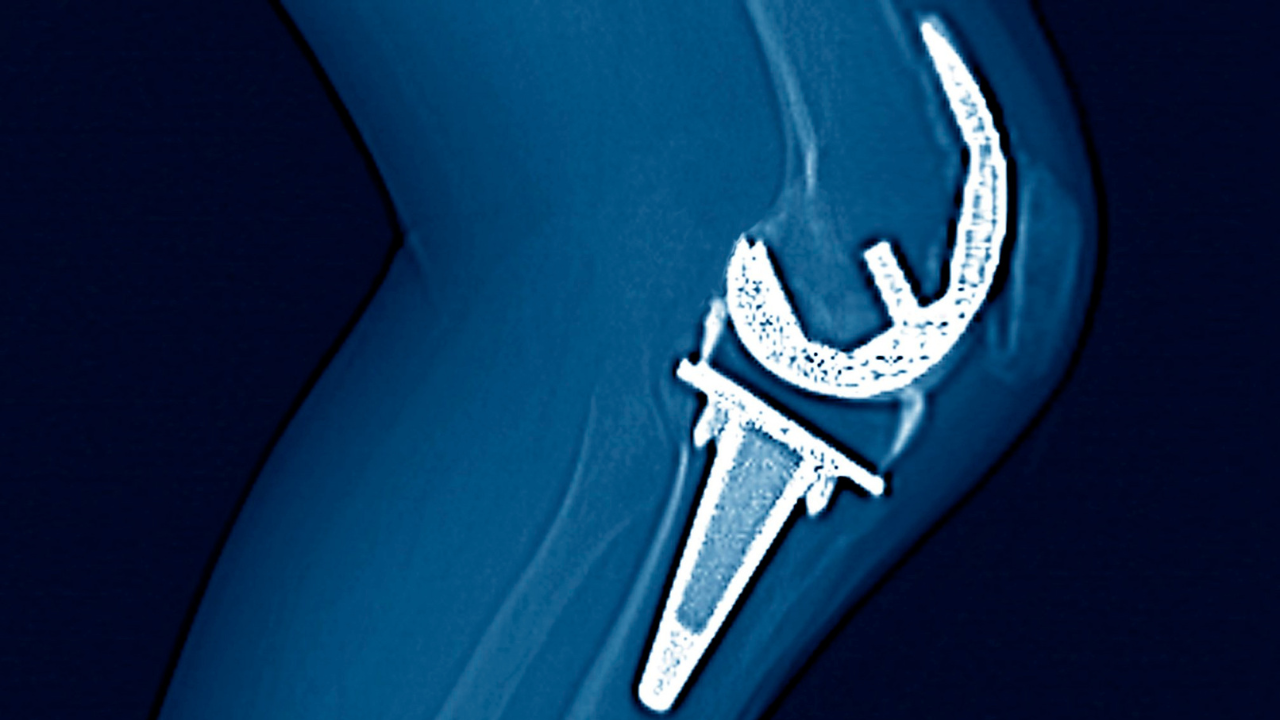
Revision Knee Replacement:
Revision knee replacement is performed when a previous knee replacement fails or wears out over time. The original prosthesis is replaced with a new one, and the procedure may involve addressing bone loss or alignment issues. This surgery is typically more complex than a primary knee replacement.
Knee Replacement Procedure
The knee replacement surgery typically follows these steps:
Anesthesia: The patient is given either general anesthesia (where they are unconscious) or regional anesthesia (where they are awake but numb from the waist down).
Incision: The surgeon makes an incision at the front of the knee to access the joint.
Resurfacing the Joint: Damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the femur, tibia, and patella (kneecap). The surfaces are then prepared for the prosthesis.
Implanting the Prosthesis: The artificial joint components made of metal, plastic, or ceramic are fitted onto the prepared surfaces.
Closure: The surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples, and the patient is taken to the recovery room for observation.
Do’s and Don’ts After Knee Replacement
Do's
- Follow your physical therapy program to regain strength and mobility.
- Use walking aids, such as crutches or a walker, as recommended.
- Keep the surgical site clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Take prescribed medications to manage pain and reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on your new joint.
Don’ts:
- Avoid high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, which can damage the new joint.
- Don’t twist or pivot on your knee immediately after surgery.
- Refrain from sitting for long periods, as this can cause stiffness in the joint.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for several weeks following surgery.
- Do not ignore any signs of infection, swelling, or unusual pain – report these to your doctor immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a knee replacement last?
A knee replacement can last 15 to 20 years or more, depending on factors such as the patient’s activity level, weight, and the type of implant used.
What is the recovery time for knee replacement surgery?
Most patients can resume normal activities within 6 to 12 weeks, but full recovery may take up to 6 months to a year.
Can I kneel after knee replacement surgery?
Kneeling may be uncomfortable after surgery, but it is generally safe. However, some patients may find it difficult to kneel due to stiffness or discomfort.
Is knee replacement surgery painful?
There will be some post-operative pain, but it can be managed with medications. Most patients report significant pain relief after recovery.
What is the difference between total and partial knee replacement?
Total knee replacement replaces the entire knee joint, while partial knee replacement only replaces one compartment of the knee. Partial replacement is less invasive and has a quicker recovery time.
What are the risks of knee replacement surgery?
Risks include infection, blood clots, implant loosening, and nerve damage. However, these risks are relatively low with modern surgical techniques.
How long will I need physical therapy after knee replacement?
Physical therapy typically lasts for 6 to 12 weeks, but some patients may require longer rehabilitation depending on their progress.
Can I drive after knee replacement surgery?
You can usually start driving 4 to 6 weeks after surgery, but this depends on which leg was operated on and how well you are recovering.
Will I need a walker or crutches after knee replacement?
Yes, most patients will need to use a walker or crutches for the first few weeks after surgery to help with mobility and balance.
Can I play sports after knee replacement surgery?
Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and golf are encouraged, but high-impact sports like running should be avoided to prevent damage to the new joint.
Discover New Heights in Healthcare with
Spire Hospital!

Address
Survey No 588, B4, 1st Floor, Ganesh Market, Jawaharlal Nehru Road, Aai Mata Mandir Chowk, Opp Market Yard Bus Depot, Bibevewadi, Pune : 411037
Phone
91759 83868
punehipandknee@gmail.com
punehipandknee@gmail.com